


Theme
Diagnostic & Interventional Radiology
INSTITUTION
-Ribat National university and Ribat university hospital,khartoum ,Sudan
Diagnostic radiology board at Sudan spechialization board,Head of training commitee ,Antalya center
Khartoum university, WHO khartoum, FMOH Khartoum

CT KUB scanning is a common diagnostic procedure. Its usefulness exceeds diagnosing renal problems to identify incidental findings that are commonly overlooked.
The aim of this study is to identify the incidental findings, its probability of occurrence and types.
This is a case series study conducted in a specialized diagnostic center in Khartoum- Sudan. The center is receiving patients from different parts of the country.As part of diagnostic process for urinary symptoms, 92 CT KUB patients were enrolled in the study during the year 2016,they were the whole patients came to CT KUB scan ,met the research crteria of sampling statedbelow.
Sampling:
Sample size:
Enrolled cases during study period are 92 individual.
Inclusion criteria:
1. Sudanese patient.
2. Patient examined in the area of study at the mentioned period of time with urological symptoms indicate investigation by CT KUB.
Exclusion criteria:
- Non Sudanese patient examined in the area of study at the mentioned period of time.
- Patent with known KUB or NON KUB pathology.
- Patient with abdominal pathology making the comment on his kidneys location, difficult or not mentioned clearly on his images report.
overall proportion of positive incidental findings among 92 patients was 12% (11 out of 92 subjects were positive). 70 cases (76%) of the subjects had positive KUB findings; nine cases of them (13%) had at least one type of incidental findings. On the other hand;22 subjects had no KUB findings; and only 2 (01%) of them had incidental findings
|
Details of incidental findings |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
|
Ovarian cyst |
4 |
4.3 |
|
|
Rectal wall thickening |
1 |
1.1 |
|
|
Psoasmuscle abscess - potts disease - causing renal obstruction |
1 |
1.1 |
|
|
Hepatomegally + ppf + PHTN |
1 |
1.1 |
|
|
Splenic calcification? old granuloma + Rt ing hernia |
1 |
1.1 |
|
|
Lumbar scoliosis + underlying degenerative discs |
1 |
1.1 |
|
|
Rt renalstone + multiple BG stones |
1 |
1.1 |
|
|
Liver cirrhosis + splenomegally + variese |
1 |
1.1 |
|
|
Osteoporosis |
1 |
1.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total of incidental findings |
12 |
13.0 |
|
|
Total of normal |
80 |
87.0 |
|
|
Total of All |
92 |
100.0 |
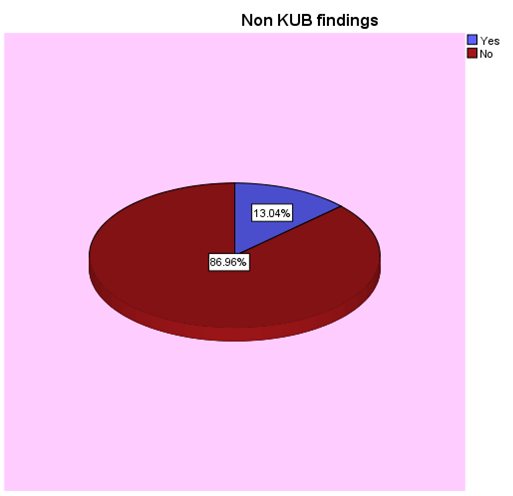
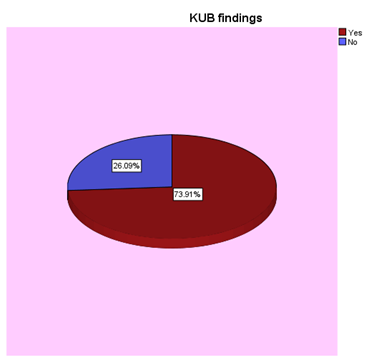
The probability of incidental findings in this study is high among patients with positive KUB findings (RR=13 times). Therefore, providing extra effort to identify incidental findings among patients having positive CT KUB findings ,aswell as patients with negative KUB findings, is essential. .
Recomendation-Take home messages:-
- State protocol for reporting CT KUB studies highlighting review of non-urinary tract structures &organs.
- CT KUB studies should be review by radiologist before patient left the department as might need contrast or more detailed imaging protocol.
- Suggest repeating the study with: Bigger sample and wide area.
References
1. Mimics of Renal colic Alternative Diagnoses at Unenhanced helical C.T. Radiographics http://pubs.org/doi/full/10.1148/rg.24si0455055
2. Smith RC, Rosenfield AT, Choe KA. Acute flank pain: comparison of non –contrast enhanced computerized tomography and intravenous pyelography. Radiology 1995, 194: 789-94.
3. Spencer BA, Dretler PS. Helical CT and ureteric colic. Urol Clin North Amer 2000, 27: 231-241.
4. Hoppe H, Studer R, Kessler TM, et al. Alternate or additional findings to stone disease on unenhanced computerized tomography for acute flank pain can impact management. J Urol 2006; 175: 1725-30.
5. Rucker CM, Menias CO, Bhalla S. Mimics of renal colic : alternative diagnosis at unenhanced helical CT. Radiographics 2004; 24:S11-S33
6. Samim M, Goss S, Weinreb J, Moore C. Incidental findings on CT for suspected renal colic in emergency department patients: prevalence and types in 5,383 consecutive examinations. J Am Coll Radiol 2015; 12: 63 -69.
.
 Send Email
Send Email