



Authors
- Chalakot Dejarkom
- Kosa Sudhorm
Institution
- Department of Radiology, Buddhachinaraj Medical Education Center, Phitsanulok, Thailand
- Department of Pediatrics, Buddhachinaraj Medical Education Center, Phitsanulok, Thailand
Team-based learning (TBL) has been applied to various courses in medical schools, and a void in the literature exists regarding the attitude of TBL in radiology. The objective of this study was to evaluate medical students’ attitudes toward TBL in radiology.


One hundred seventy nine 5th year medical students in Buddhachinaraj Medical Education Center in elective course of radiology in academic year 2010-2013 were studied topic gastrointestinal radiology by TBL method. At the end of the course, they were surveyed for their attitudes toward TBL in radiology by using 10 (five rating scale) questionnaire items. Data were analyzed for frequency, percentage, mean and standard deviation.
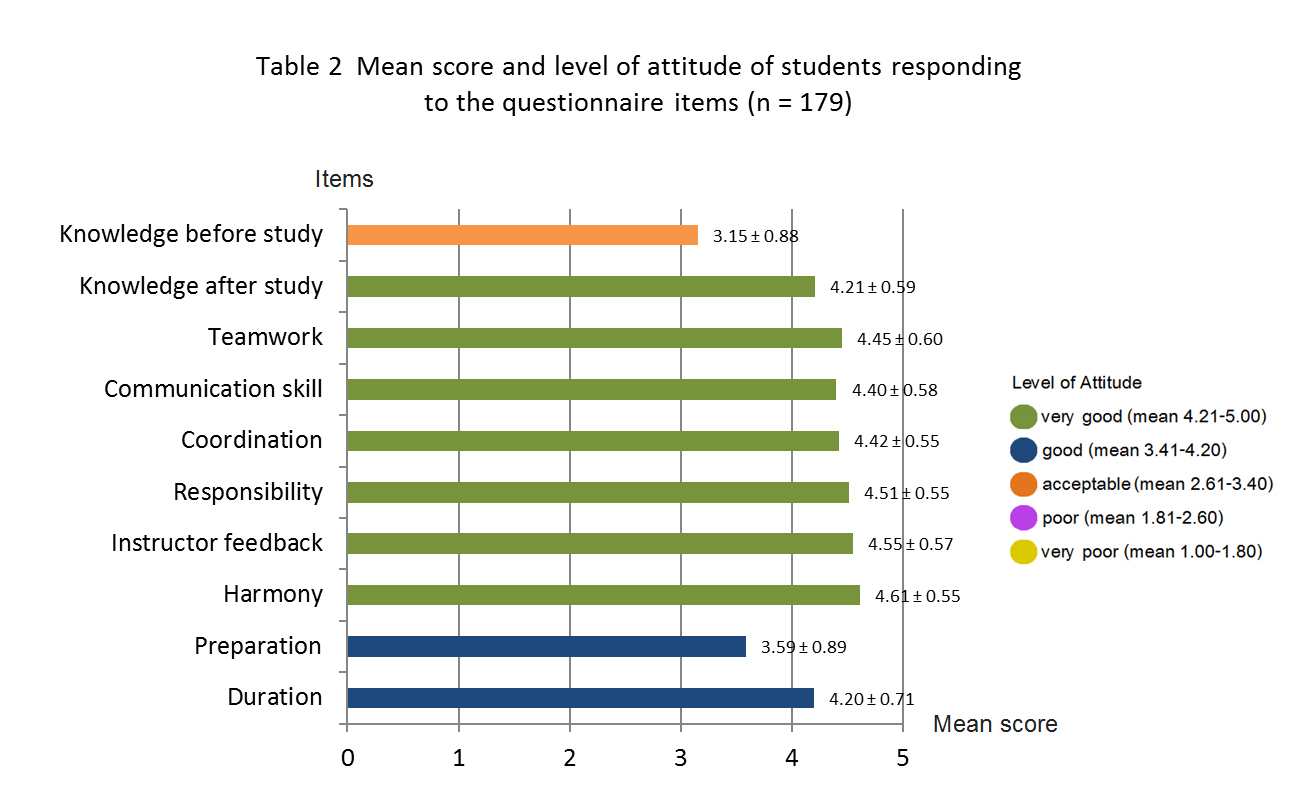 The level of attitudes was very good (mean > 4.21) for knowledge after study, teamwork, communication skill, coordination, responsibility, instructor feedback and harmony. The level of attitudes was good (mean 3.41 - 4.20) for preparation and duration. The level of attitudes was acceptable (mean 3.15) for knowledge before study. Mean T-RAT scores was significantly higher than mean I-RAT scores (70.39 ± 9.84, 33.41 ± 15.57, p < 0.001).
The level of attitudes was very good (mean > 4.21) for knowledge after study, teamwork, communication skill, coordination, responsibility, instructor feedback and harmony. The level of attitudes was good (mean 3.41 - 4.20) for preparation and duration. The level of attitudes was acceptable (mean 3.15) for knowledge before study. Mean T-RAT scores was significantly higher than mean I-RAT scores (70.39 ± 9.84, 33.41 ± 15.57, p < 0.001).
The results reveal that medical students’ attitudes toward TBL in radiology are good to very good.
TBL is one of the good choice study method in radiology.
- Buranachokpaisan C, Sudhorm K, Dansawang S. Can we do an attractive elective radiology course? Proceedings of AMEE 2013; 2013 Aug 24-28; Prague, Czech Republic.
- Michaelsen LK, Fink LD, Knight A. Designing effective group activities: lessons for classroom teaching and faculty development. In: DeZure D, editor. To improve the academy: resources for faculty, instructional and organizational development. Stillwater: New Forum Press; 1997. p.31-58.
- Dejarkom C, Sudhorm K. Medical students’ learning outcomes between team-based learning and lecture-based learning in radiology. Buddhachinaraj Med J 2010;27(3):411-6.
- Parmelee DX, DeStephen D, Borges NJ. Medical students’ attitudes about team-based learning in a pre-clinical curriculum. Med Educ [serial online] 2009 [cited 2013 May 15];14:1-7. Available from: http://www.med-ed-online.org
- Thompson, BM, Schneider VF, Haidet P, Levine RE, McMahon KK, Perkowski LC, et al. Team-based learning at ten medical schools: two years later. Med Educ 2007;41:250-7.
- Touchet BK, Coon KA. A pilot use of team-based learning in psychiatry resident psychodynamic psychotherapy education. Acad Psychiatry 2005;29:293–6.
- Hunt DP, Haidet P, Coverdale JH, Richards B. The effect of using team learning in an evidence-based medicine course for medical students. Teach Learn Med 2003;15:131-9.
- Koles P, Nelson S, Stolf A, Parmelee D, Destephen D. Active learning in a Year 2 pathology curriculum. Med Educ 2005;39:1045-55.
- Nieder GL, Parmelee DX, Stolf A, Hudes PD. Team-based learning in a medical gross anatomy and embryology course. Clin Anat 2005;18:56-63.
- Seidel CL, Richards BF. Application of team learning in a medical physiology course. Acad Med 2001;76:533-4.
- Sudhorm K, Ardonk W. Team-based learning in pediatric department, Buddhachinaraj Medical Education Center. Buddhachinaraj Med J 2008;25(1):5-11.
- Tunnitisupawong T, Sudhorm K. The effectiveness of team-based learning in medical students. Proceedings of AMEE 2007; 2007 Aug 27-29; Trondheim, Norway.
- Sudhorm K, Klanarong S. Team-based learning in Pediatric Department, Buddhachinaraj Medical Education Center: 2 years comparative study. Proceedings of AMEE 2010; 2010 Sep 4-8; Glasgow, United Kingdom.
- Inuwa IM. Perceptions and attitudes of first-year medical students on a modified team-based learning (TBL) strategy in anatomy. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J 2012;12(3):336-43.
- Michaelsen LK, Black RH. Building learning teams: the key to hamessing the power of small groups in higher education. In: Kadel S, Keehner J, editors. Collaborative learning: a sourcebook for higher education. Vol 2. State Collarge: National Center for Teaching, Learning and Assessment; 1994. p.65-81.

