


Theme
3II International
INSTITUTION
Mie University Graduate School of Medicine - Center for Medical Education
Mie University
University of Zambia



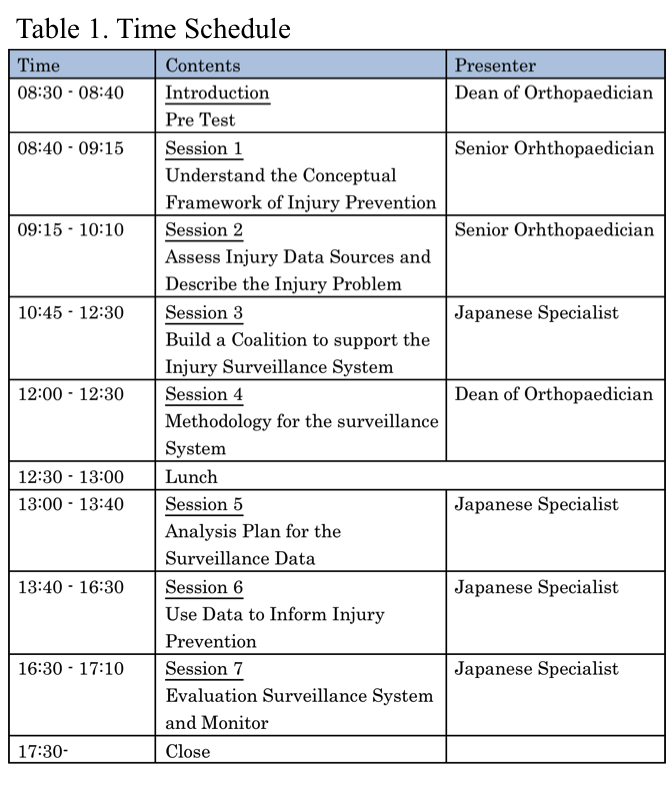
Assesment:
1) pre-test and post-test (before and after the workshop to measure injury knowledge)
2) questionnaires about present injury situation
3) interviews about this workshop

 |
  |
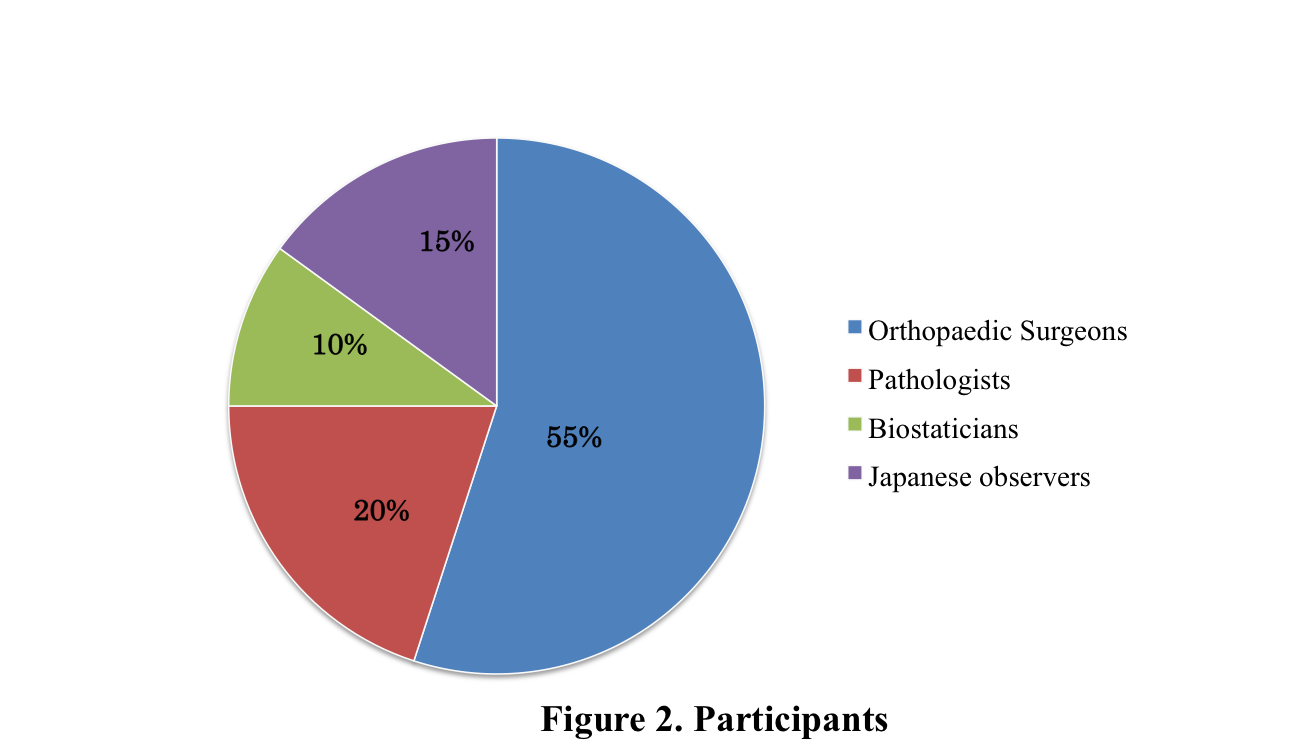
8 orthopedic surgeons and 2 pathologists have completed the tests (pre and post) and qestionnarie.
6 junior and 4 senior doctors (more than 5 year experience)
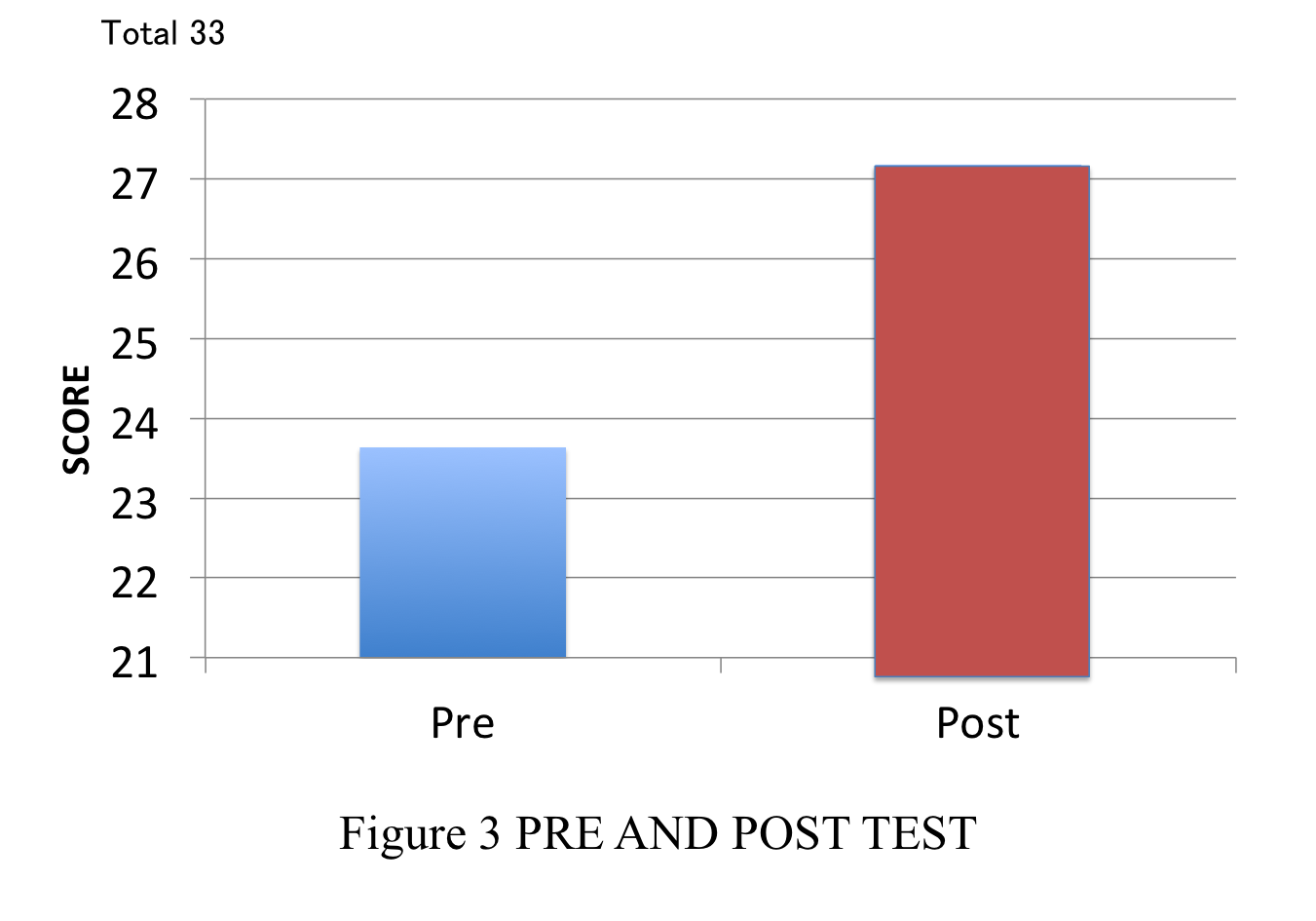
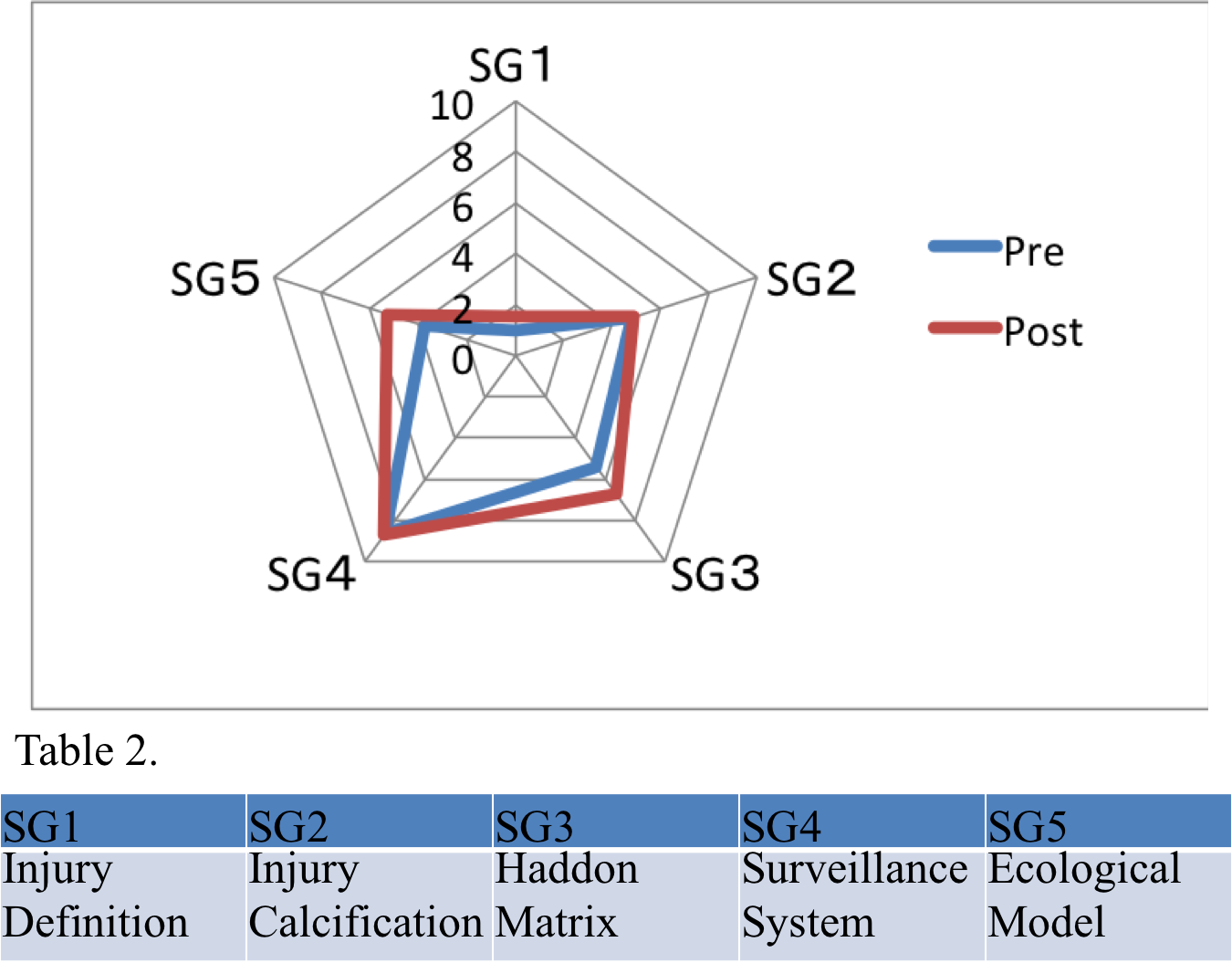
1) Pre-test and post-test evaluation average score increased by 10.7%. (P<0.005)
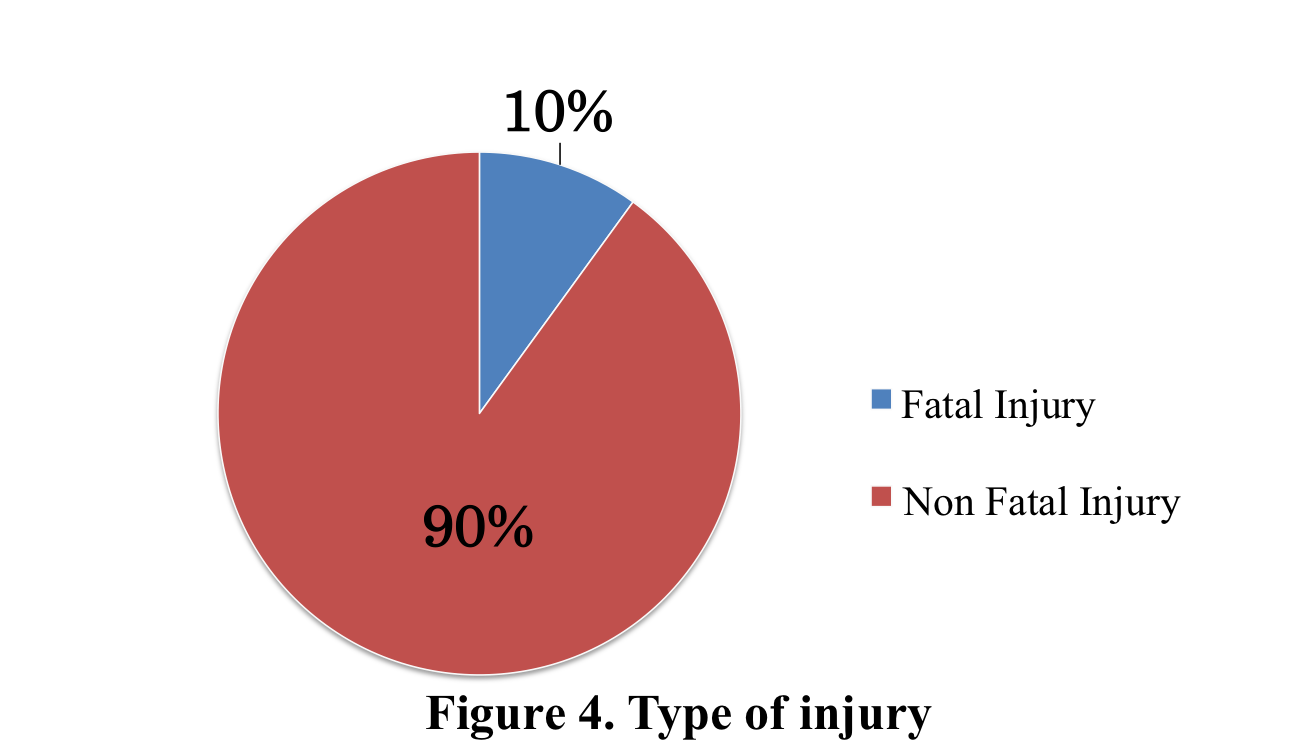
2) 6 junior doctors had to go to multiple departments to treat the patients (emergency room, inpatient ward, outpatient ward and mortuary).
3) For biostatisticians it was a good opportunity to meet with doctors and see the flow of data gathering and entry. Japanese observers learned different teaching skills.
 |
 |
 |
 |
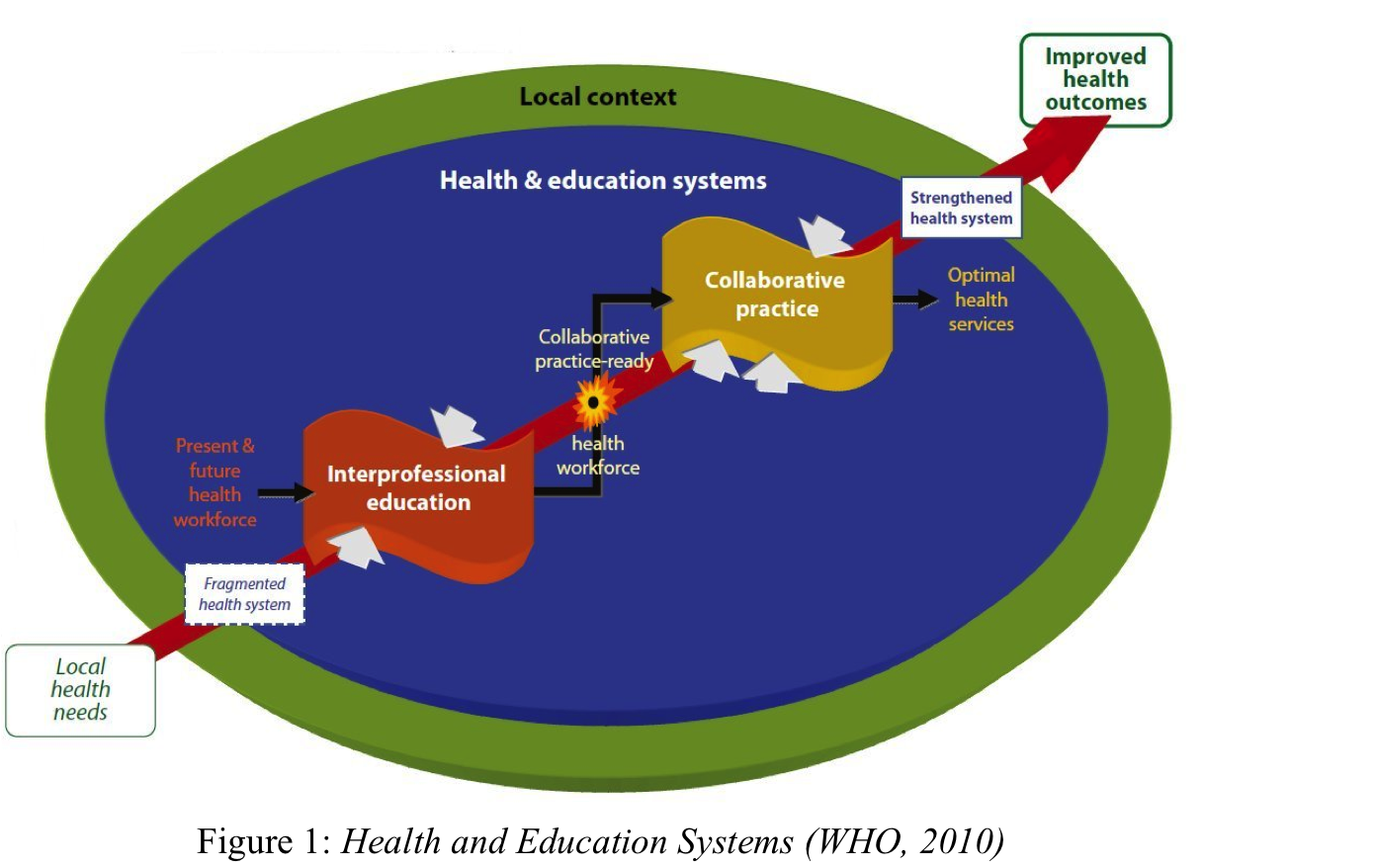
According to WHO implementation of integrated health workforce strategies. Health system and Education System transformation are essential.
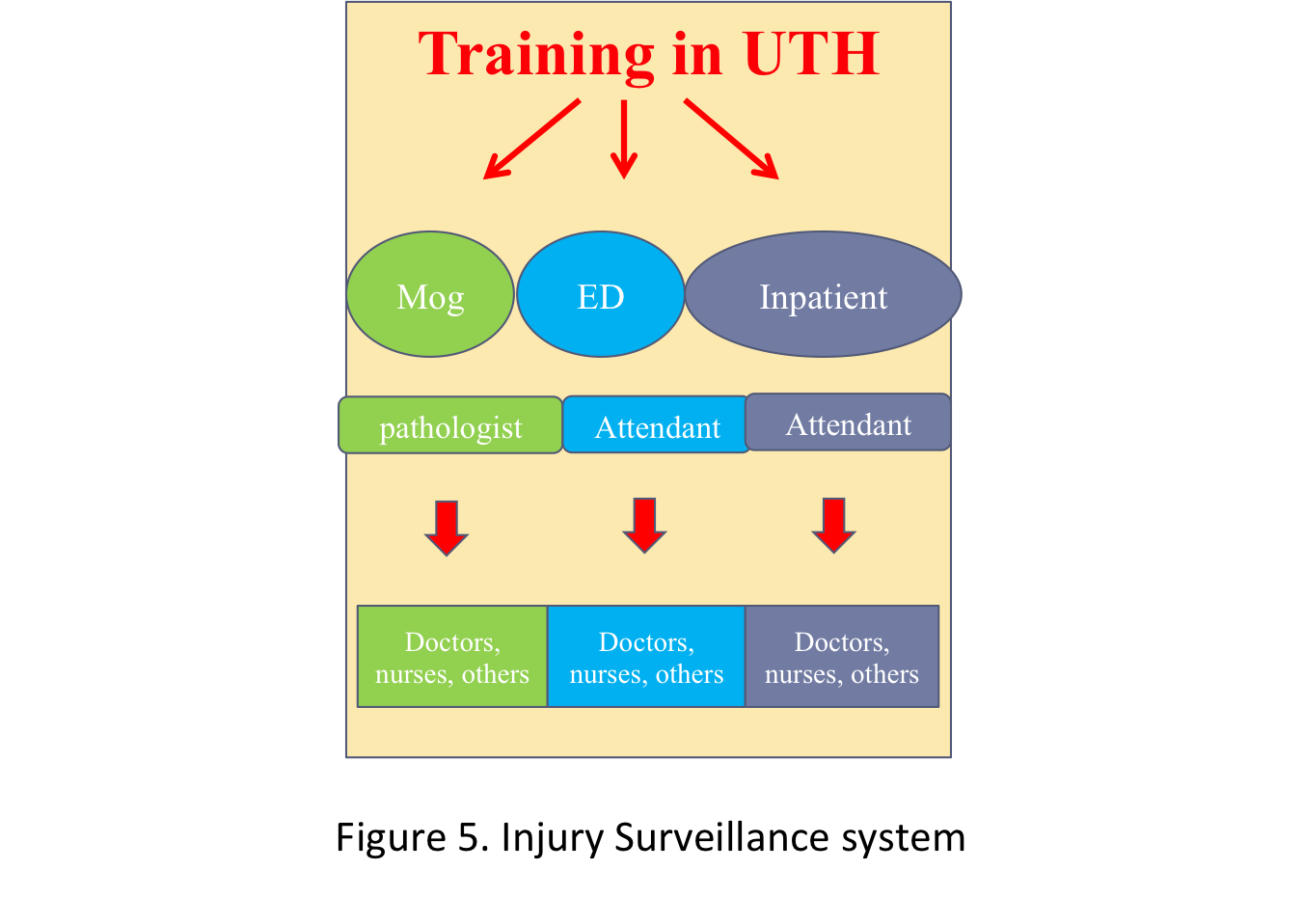
We also confirmed interprofesional eduation and collaborative work was needed for better Injury surveillance system.
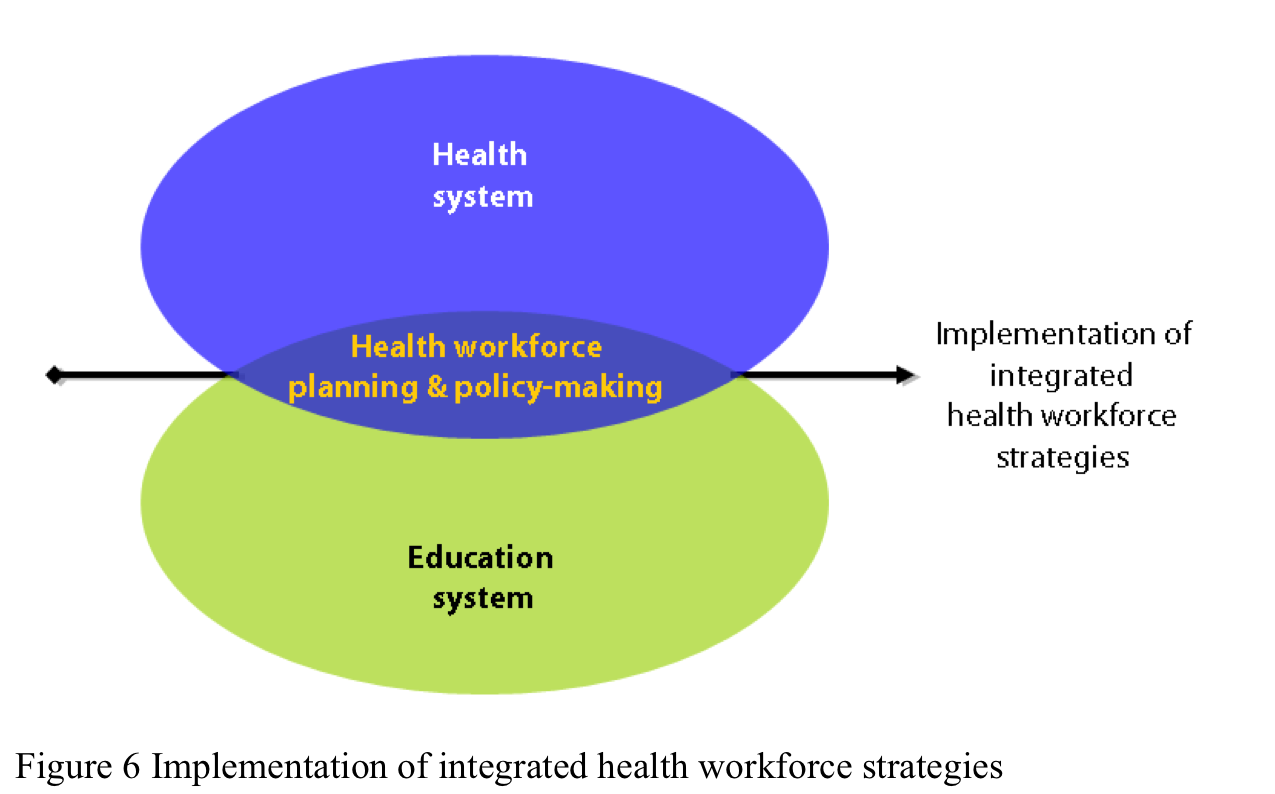
Developed country and emerging country collaboration is challenging, interprofessional collaboration between different health professions is effective to develop sustainable partnerships.

1. WHO Framework for Action on Interprofessinal Education & Collaborative Practice 2010
2.WHO Fatal Injury surveillance in mortuaries and hospitals a manual for practitioners 2012
3. Injury Surveillance Training Manual CDC
 Send Email
Send Email