



Theme
eLearning
INSTITUTION
Division of Medical Education, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada
.jpg)





What has becoming fully distributed meant to us at Dalhousie?
Lots of changes!
A significant consideration is the adoption and integration of new technologies, including:
1. a state-of-the-art telepresence (videoconferencing) system;
2. the increasingly paperless delivery of our curriculum; and
3. the use of electronic teaching cases, assessment tools, and curriculum management systems.
We are a "living lab!"
Our goal is to address the research question: How is technology-focused curriculum renewal experienced by students, faculty & staff?
How are we exploring this question?
We are using a sophisticated qualitative methodology.
We are conducting a three-year institutional ethnography (Smith, 2005) informed by insights from sociomaterial theory (Ajjawai & Bearman, 2012) including actor-network theory (Latour, 2005).
Our study benefits from a large and diverse research team with a variety of skill sets and areas of expertise.
Our methods include:
A comprehensive textual analyses of documents and policies related to undergraduate medical education and learning technologies.
In-depth observations of technologically-mediated events (lectures, small-group learning, committee meetings, etc.).
In-depth interviews with faculty, staff and students.
What do we mean by "sociomateriality?"
Social Considerations:
Social issues have received significant attention in medical education.
This includes things like relationships and affective learning.
Material Considerations:
These have not been explored in detail in medical education.
The material becomes very important when considering technology and distributed learning.
“The material world includes tools, technologies, bodies, actions, texts, discourse and objects, treated as continuous with and embedded in human relations”
–Ajjawi & Bearman (2012)
Education is Digital!
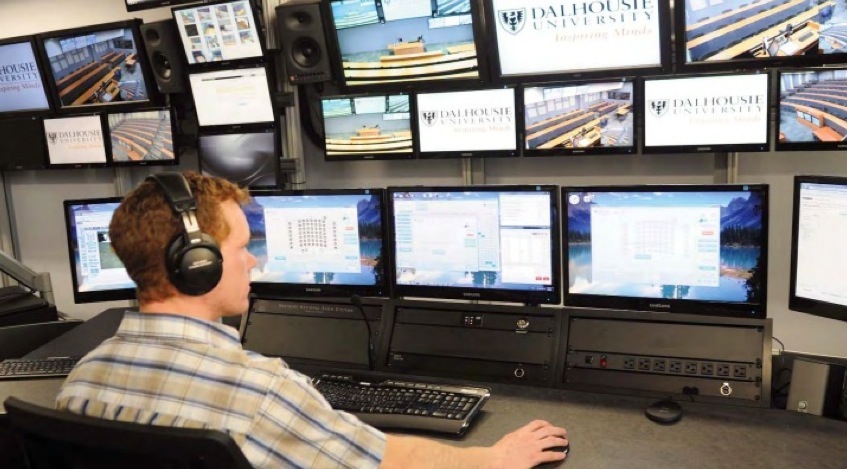

Education is Social


Education is Material





What are we learning?
- We are learning that matter matters (available technologies, classroom spaces, placement of videoconferencing cameras etc.).
- Relatedly, material conditions also are highly important (the geography of our institution, availability of technicians to monitor videoconferencing, access to mobile devices, access to internet connections, barriers imposed by firewalls, etc.).
- Matter does not exist in isloation of the social!
The sociomaterial matters!
- An individual learner is enmeshed in a network of influential factors, both human and non-human. (Bleakley, 2012)
- Optimizing digital medical education requires an understanding of this network of social and technological influences.
- While we’ve long recognized the importance of social learning in medical education, material conditions have been largely ignored.
- We are learning that both social (relationships) and material (technological) contexts have a significant influence on learning.
![]()
Ajjawi, R. & Bearman, M. (2012). Sociomateriality matters to family practitioners as supervisor. Medical Education, 46 (12), 1145-1147.
Bleakley, A. (2012). The proof is in the pudding: Putting Actor Network Theory to Work in Medical Education. Medical Teacher, 34(6), 462-467.
Latour, B. (2005). Reassembling the Social: An Introduction to Actor-Network Theory. NY: Oxford University Press.
Smith, D. (2005). Institutional ethnography: A sociology for people. Toronto, ON: AltaMira Press.
 Send Email
Send Email