
| Theme: Patient Safety | |||
 |
||||||
| Patient safety and quality leadership scholars program: Creating human infrastructure for teaching safety and quality |
 |
|||||
|
||||||
1. Formal curriculum
Formal sessions were conducted in weekly 3.5 hour afternoon seminars over a 5 month period. University of Michigan Faculty and visiting faculty with expertise in quality and safety leadership and research conduct these weekly sessions. Sessions are designed to be interactive, supported by readings and application exercises. Core components of the curriculum include the following:
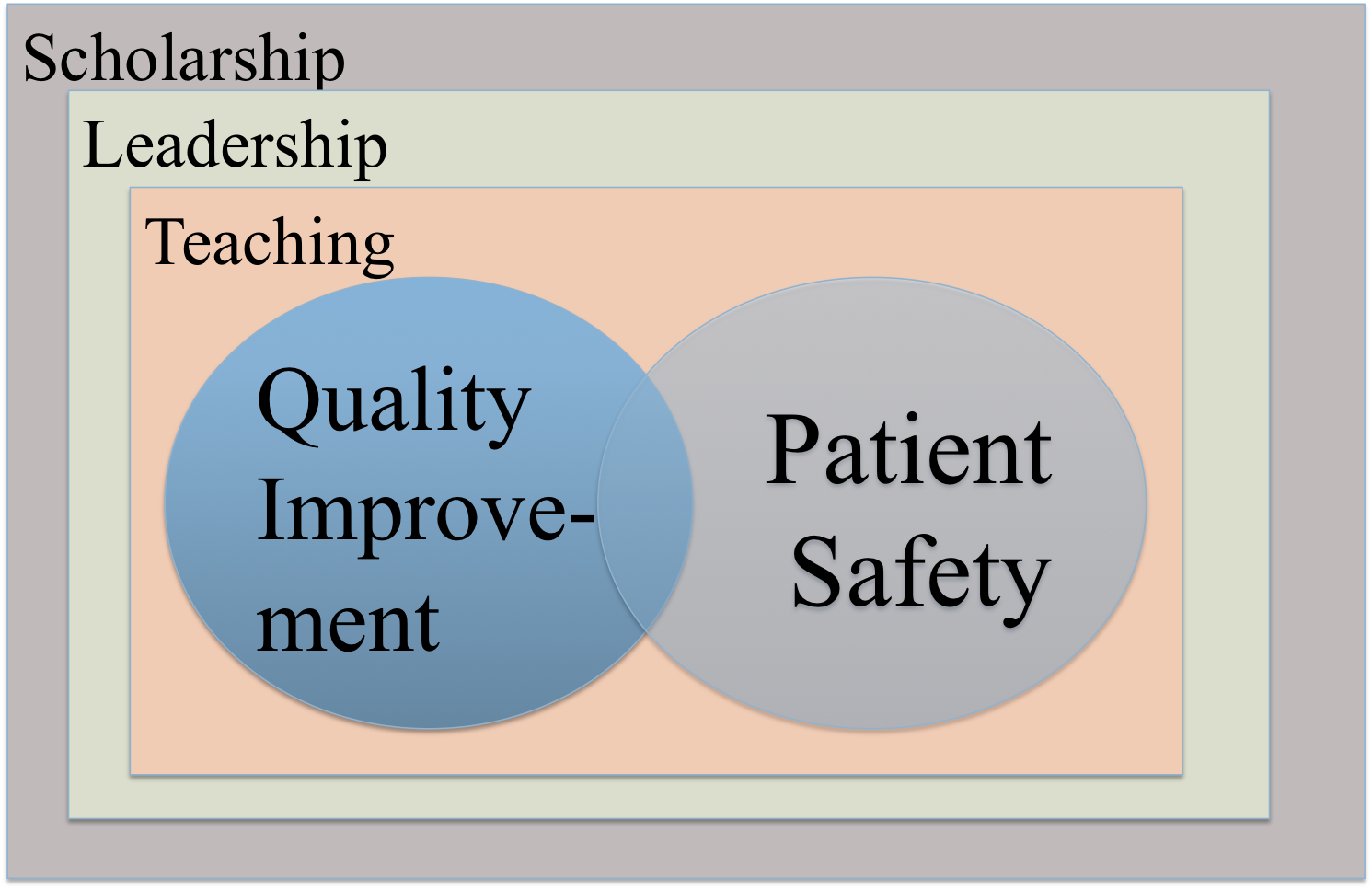
Quality Improvement: a solid understanding of quality improvement theory and practice, including the Michigan Quality System’s Lean Thinking principles and methods, as well as other approaches to quality improvement.
Patient Safety: safety science, including systems theory; theories of error and resilience; root cause analysis; and non-technical skills such as communication and teamwork.
Leadership: an understanding and skills to align and lead the implementation of safety and quality programs, including leadership skills, strategic alignment of goals, organizational change, group work, and mentorship.
Teaching: educational theory and practical techniques applied to teaching others formally and informally about basic principles and methods for improving safety and quality in patient care.
Scholarship: methods for applied research and evaluation studies in quality and safety, exploration of research trends, and the presentation and publication of scholarly work in safety and quality.
2. Consultants and Visiting Faculty
The Scholars have access to quality and safety experts who serve as consultants to guide the Scholars through the program and advise and assist them with their quality and safety projects as needed. The consultants include experts at the University of Michigan as well as visiting faculty from outside the University.
3. Hands-on Project
Scholars identified a new or existing issue in quality or safety relevant to their interests and developed or refined the project to improve safety and/or quality. This project provided the scholar with an opportunity to apply the principles, skills, and methods acquired in the program and to develop a scholarly approach to safety and quality. Scholars were expected to present projects and their results at local, regional, and national quality and safety meetings.
4. Peer Group of Scholars
The scholar cohort share formal learning sessions, work together in small group approaches to learning, and interact and collaborate with each other on safety and quality issues and projects. The peer group of scholars will expand as additional faculty participate in future offerings of the program.
Participants’ Areas of Specialty
• OB/GYN
• Emergency Medicine
• General Medicine (Hospitalist)
• Pediatrics (NICU)
• Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
• Pathology
• Otolaryngology
• Anesthesiology
Safety and QI Projects (examples)
• Pathology lab OPPE quality metrics
• Multi-disciplinary rounds
• On-time starts of scheduled cesarean deliveries
• Handoffs in the Emergency Department
• Discharge summary process
• Medication reconciliation process
• Case-review process
• Tracheostomy care
Strengths
Addresses an institutional need for teachers of QI
Area for improvement
Feasibility of maintaining program, and transfer to other settings
This scholars program provides an effective model curriculum for developing the human capital needed to teach PS/QI.

For more information, please contact: jseagull@umich.edu

 Send Email
Send Email