
| Theme: Radiation Oncology | |||
 |
||||||
| Involved-site radiation therapy by Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy versus 3D- conformal radiotherapy for treatment of stages I & II supra-diaphragmatic Hodgkin`s lymphoma |
 |
|||||
|
||||||
Introduction:
Involved Site Radiation Therapy (ISRT) decreased the volumes of lungs, breasts and thyroid that receiving high dose radiation, VMAT delivers highly conformal radiotherapy giving the potential to reduce long term toxicity, without effect on local control.
Aim of the work
Our aim is to compare between VMAT and 3D conformal radiotherapy for treatment of ISRT in cases of early stage supra-diaphragmatic HL
Patients and methods:
34 patients affected with stages I and II supra-diaphragmatic HL, treated between January 2011 and September 2015 with combined modalities therapy.
CTV was contoured based on the pre-chemotherapy CT and PET-CT scans and modified according to anatomical changes. Organs at risk like heart, breasts, lung, spinal cord, thyroid and parotid were delineated. Patients were given 30 Gy as 2 Gy/fraction over 3 weeks period. The PTV received ≥ 95% and maximum dose ≤ 115% of the prescribed dose. The 3-DCRT plans two parallel opposing with MLC shaping and VMAT plan consisted of either single full arc (360°) plan or double arc plan.
Results:
After a median follow up period of 30 months, PFS and OS in both groups were 100%. No statistically significant deference between the acute radiation toxicities in both groups with Oropharyngeal mucositis the commonest.
The mean dose for lung was higher in 3D-CRT than VMAT (12.0 ± 6.1 Gy vs. 9.9 Gy ± 8.6 Gy). For the breasts volume, the V5Gy was slightly higher for 3D-CRT compared with VMAT (7.6% and 6.5%) respectively. For the heart, V5Gy and V10Gy values were higher for the RA than for 3D-CRT accounting for (51.9 ± 28.9%) and (41.0 ± 24.6%) versus (40.0
± 25.9% and 30.7 ± 22.5%) respectively. Thyroid gland mean dose was lower for VMAT (21.8 ± 7.7 Gy) than for 3D-CRT (26.8 Gy ± 4.1 Gy) but did not reach statistically significant value (P = 0.06).The mean doses in both 3D-CRT and VMAT were similar at, 29.5% and 30.5% respectively, with no statistically significant deference. Also, the dose coverage for the PTV in both techniques was optimal as indicated by V90%, V95% and V107% values.
For the parotids the mean doses were statistically significant lower for VMAT.For thyroid gland The Dmax and V30 in VMAT was significantly lower than that for 3D-CRT.
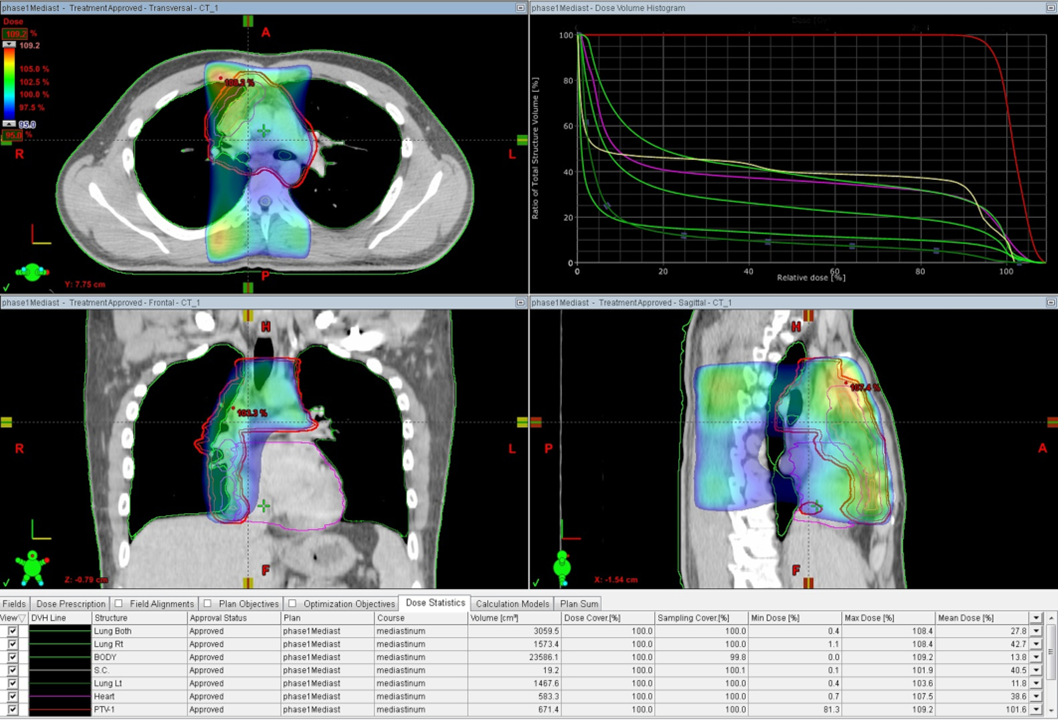
Fig (1)
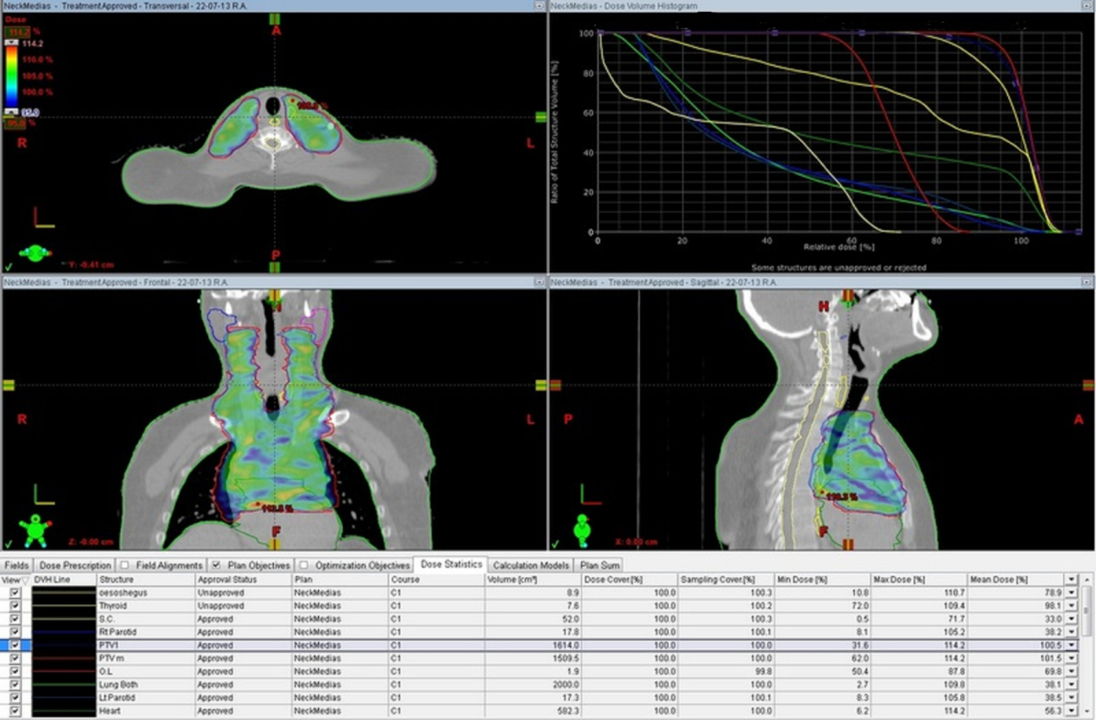
Fig (2)
Dose distribution for 3D-CRT plan, Fig (1) and for VMAT, Fig (2) in the transversal, sagittal, and coronal plane for a patient with typical PTV involving the superior mediastinal lymph nodes, involving cervical and mediastinal lymph nodes respectively, Dose volume histogram data is included.
Conclusion:
•Our study shows that reduction of target volume to ISRT most effectively improves OAR sparing, regardless of the radiation technique used.the mean doses to the lungs, thyroid, parotids and esophagus were lower in VMAT technique than in 3D-CRT.
Both techniques are equivalent in disease control and the selection should be individualized according to clinical circumstances. Further studies for the use of VMAT in HD disease is required to assess the long term side effects.

 Send Email
Send Email