


Theme
5BB Team Based Learning/Learning anatomy
INSTITUTION
Medicine - Thailand
Medicine - Surgery - Thailand
Medicine - Family and Community - Thailand



Team-based learning (TBL) and problem-based learning (PBL) have been widely exercised as effective methods to promote active learning in medical education. However, a small body of research has been regarding the application of both methods among Thai medical students. The aim of the study was to compare satisfaction towards these methods among third-year medical students at Suranaree University of Technology, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand.
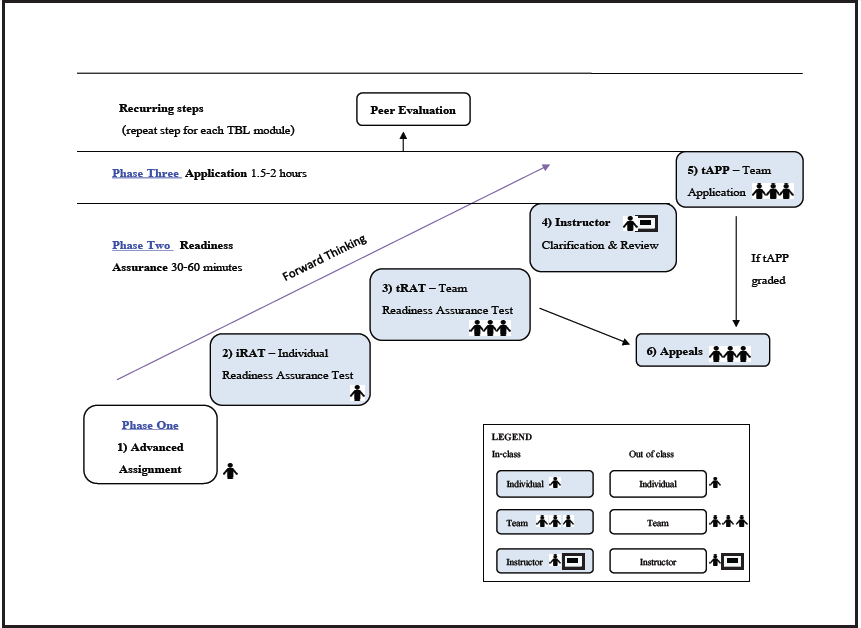
The study incorporated 60 third-year medical students who enrolled in a two-week course in Gastrointestinal System, which employed an integrated TBL and PBL approach. Student satisfaction towards these two learning methods was evaluated by questionnaires upon completion of the course. Data were analyzed using the two-sample t-test.
Parmelee D, Michaelsen LK, Cook S, et al. Team-based learning: a practical guide: AMEE guide no. 65. Medical Teacher 2012; 34(5), e275-87. [PMID: 22471941]
Michaelsen LK, Davidson N, Major CH. Team-Based learning practices and principles in comparison with cooperative learning and problem-based learning. Excellence in College Teaching 2014; 25(4).
Altintas L, Altintas O, Caglar Y. Modified use Team-based learning in an ophthalmology course for fifth-year medical student. Adv Physiol Educ 2014; 38(1), 46-8. [PMID:24595469]


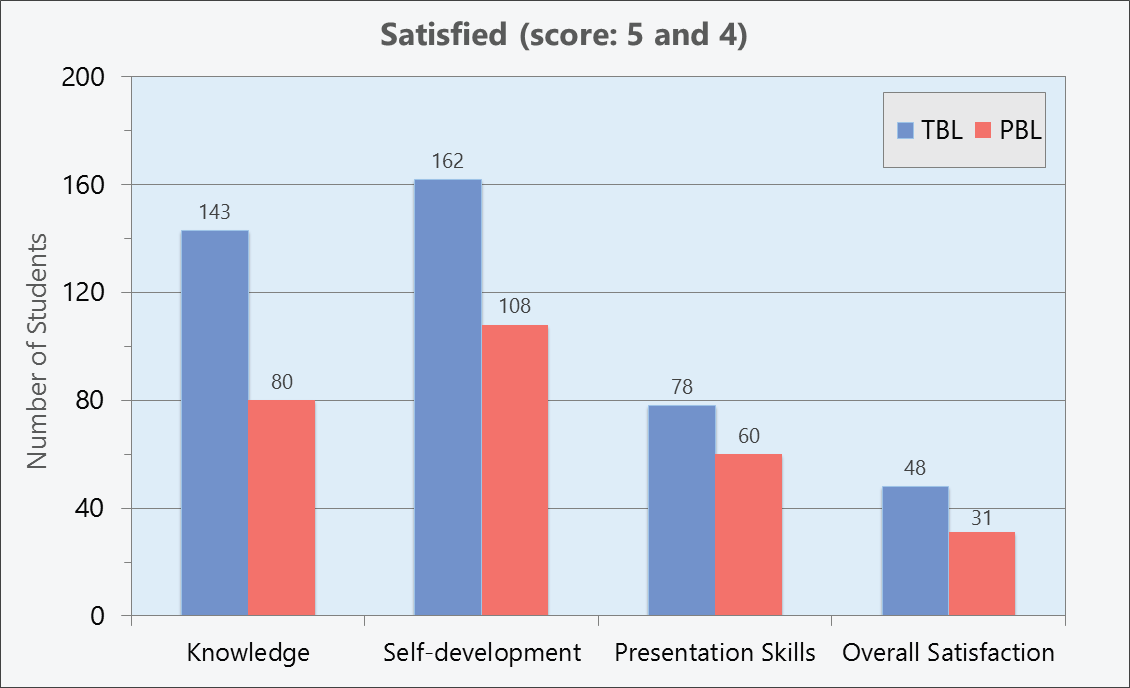
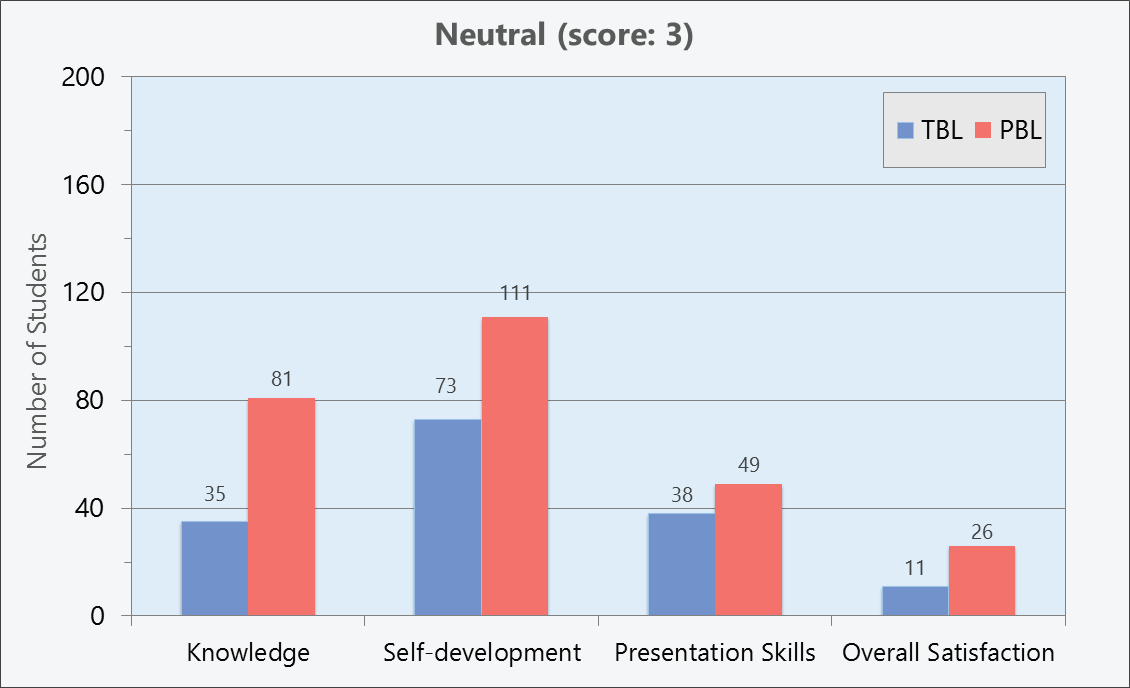
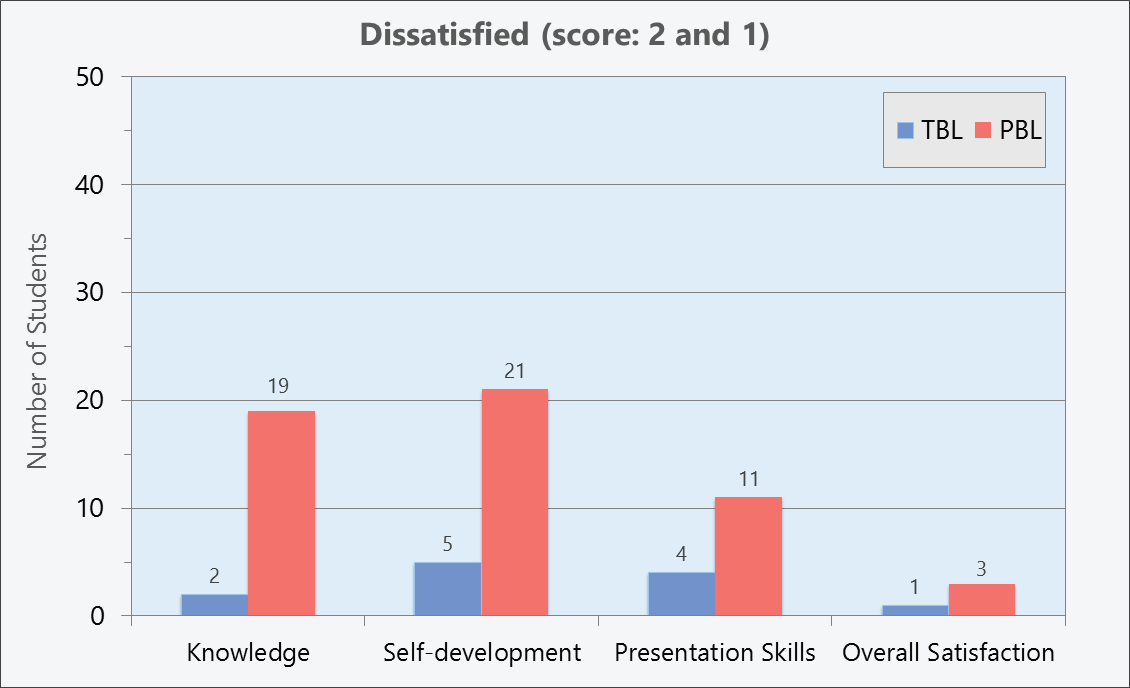
Significant difference was found between student satisfaction towards TBL and PBL in the following categories: knowledge (understanding of learning content, application of pre-clinical knowledge, a variety of knowledge from instructors), self-development (confidence to search for medical information, confidence to solve unexpected problems, eagerness to learn), presentation skills (oral presentation, confidence to work as a team), as well as overall satisfaction (p <0.05). However, the study revealed no significant difference of satisfaction scores in terms of the holistic view of patients (p=0.053).
Our study revealed that the majority of the students were more satisfied with TBL than PBL
The study showed that TBL was more efficient than PBL in the students’ opinion.
This study was supported by a grant for medical investigation from Suranaree University of Technology. We thank all medical students who participated in the study.
Correspondence to: Dalad Phromphan, Institute of Medicine, Suranaree University of Technology, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand. Tell +66 85 499 4887 E-mail: daladphromphan@gmail.com
 Send Email
Send Email