


Theme
10AA Surgery
INSTITUTION
Far Eastern Memorial Hospital - Department of Medical Education - New Taipei City - Taiwan
Far Eastern Memorial Hospital-Center of Cardiovascular -New Taipei City-Taiwan
 Healthcare Matrix (HM) is a six-by-six matrix that links to the ACGME core competencies and the IOM dimensions of quality as a tool to improve health care. The matrix provides a blueprint to help residents to learn the core competencies in patient care. We implemented HM in grand rounds (GR) and mortality and morbidity conferences (M&M) to enhance surgical residents’ competency development and patient care capabilities.
Healthcare Matrix (HM) is a six-by-six matrix that links to the ACGME core competencies and the IOM dimensions of quality as a tool to improve health care. The matrix provides a blueprint to help residents to learn the core competencies in patient care. We implemented HM in grand rounds (GR) and mortality and morbidity conferences (M&M) to enhance surgical residents’ competency development and patient care capabilities.
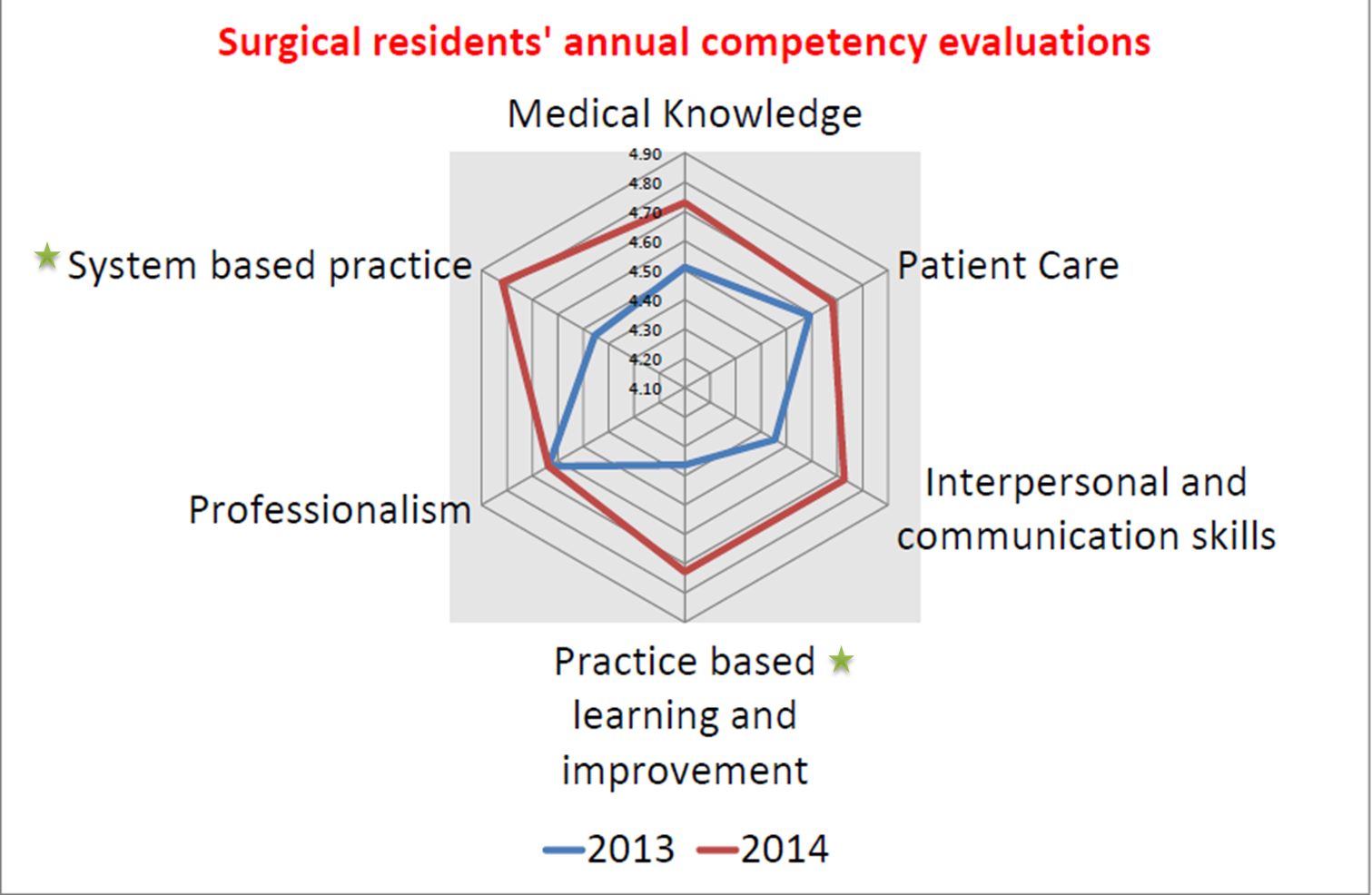 Comparing 2013 and 2014 surgical residents’ annual competency evaluations revealed all of these competencies had got improvements in which “practice-based learning and improvement “and “system-based practice” have got statistic significant (p<0.05). Reviewing six medical quality indicators retrospective and made the comparisons between 2013 and 2014, we found five indicators showed improved except the rate of completed inpatient consultation within 24 hours”, “completed discharge note within 3 days” to review that HM could help the residents to link mastery of the competencies with improvements in quality of care.
Comparing 2013 and 2014 surgical residents’ annual competency evaluations revealed all of these competencies had got improvements in which “practice-based learning and improvement “and “system-based practice” have got statistic significant (p<0.05). Reviewing six medical quality indicators retrospective and made the comparisons between 2013 and 2014, we found five indicators showed improved except the rate of completed inpatient consultation within 24 hours”, “completed discharge note within 3 days” to review that HM could help the residents to link mastery of the competencies with improvements in quality of care.
Implementation of HM with faculty professional collaborative efforts covers quality of patient care and of clinical education. It is worthy of consideration to be used in other medical fields.
 Residents in department of surgery had used HM to review all M&M and GR cases with all faculty members since 2013. We applied the annual six core competencies evaluation by their training program directors to exam their competency achievements. Moreover, we surveyed six medical quality indicators which were “prolonged admission over 30 days”, “outpatient antibiotic using rate”, “returned to ED within 3 days after discharge”, “against medical advice discharge”, “completed inpatient consultation within 24 hours”, “completed discharge note within 3 days” to review that HM could help the residents to link mastery of the competencies with improvements in quality of care.
Residents in department of surgery had used HM to review all M&M and GR cases with all faculty members since 2013. We applied the annual six core competencies evaluation by their training program directors to exam their competency achievements. Moreover, we surveyed six medical quality indicators which were “prolonged admission over 30 days”, “outpatient antibiotic using rate”, “returned to ED within 3 days after discharge”, “against medical advice discharge”, “completed inpatient consultation within 24 hours”, “completed discharge note within 3 days” to review that HM could help the residents to link mastery of the competencies with improvements in quality of care.
The achievements of implementation HM are particularly encouraging. HM discussions can facilitate surgical residents’ competency developments and were used to improve the quality of health care service.
 Send Email
Send Email