


Theme
2II Evaluation of teaching/Educational research
INSTITUTION
Universidad Autónoma de Chihuahua School of Medicine - Research Department

The knowledge society and the global health problems, require physicians with different professional practice. The challenge is for the performance of the medical teacher.
The aim is to show medical teacher competences and its relation with student academic performance.
- AMFEM (2012). Competences Profile of Professor of Medicine.
- R. Mora, JG. (2004). The need for educational change knowledge society. Revista Iberoamericana Education (35), pp. 13-37.
- A. Parra, H; A. Vázquez, A D and Del Val O., N. (2012). Competences curriculum evaluation. Perspective of students and teachers. Editorial Académica Spanish.
- Simone R., D; Hersh S. H. (2006). The key to personal, social and economic welfare competencies, Málaga, Andalucía Open Learning, Consorcio Fernando de los Ríos, 2006. Vol. 6. Spain.
- Tobon T., S. (2013). Comprehensive training and competences. Complex thinking, curriculum, teaching and assessment. Eco editions. CIFE Institute. Colombia.
- Velaz, Vaillant C, D (2009). Learning and teacher professional development. Educational Goals 2021 OEI. Fundación Santillana.
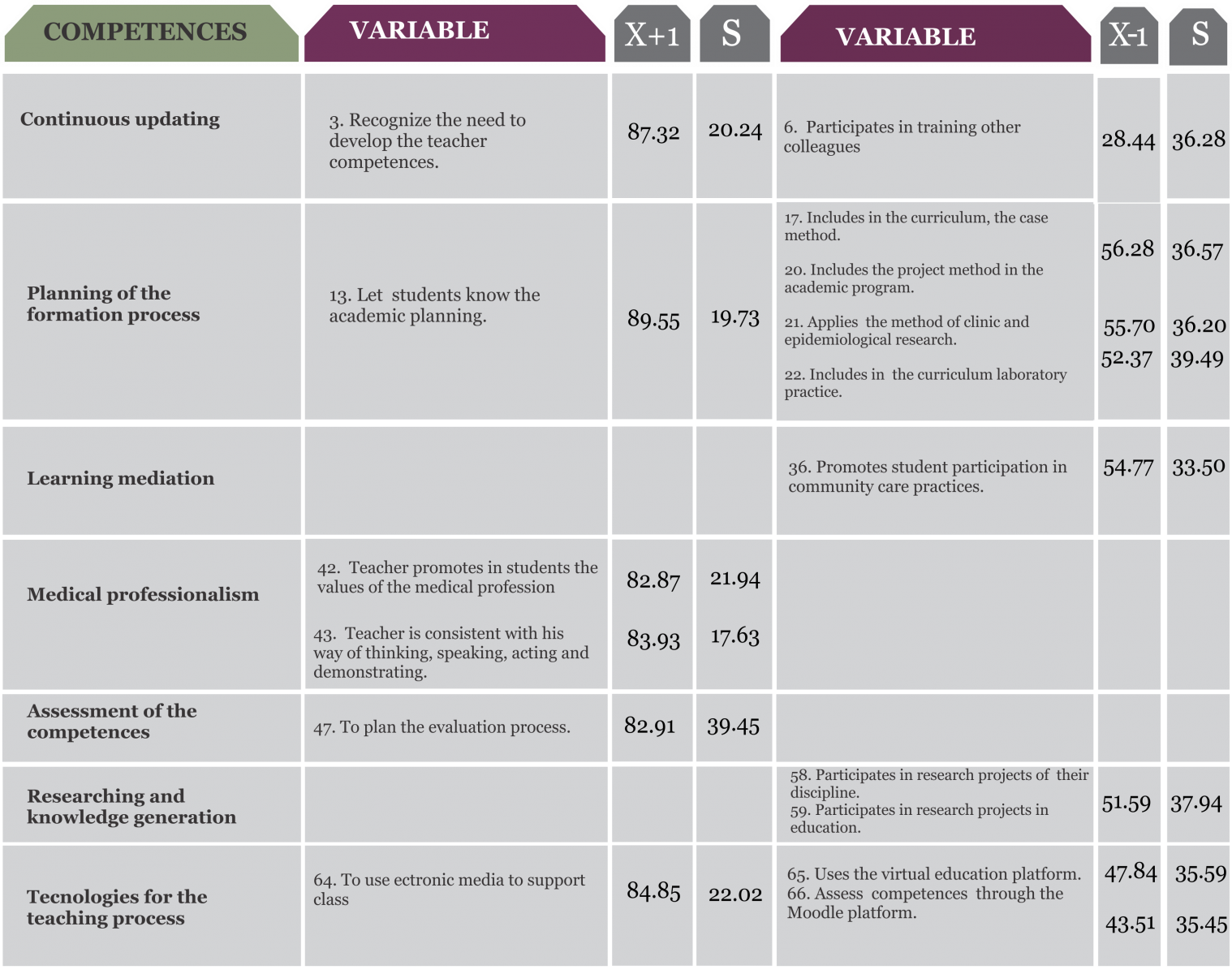
According to the results obtained, teacher competences best evaluated were: planning, continuous training and promoting professionalism. However the teacher´s competences that were less valued were: investigation, teaching intervention and evaluation that influenced the academic performance of medical students.
We found a significant correlation between recognizing the development of teaching competences and contribuiting to the formation of creative and innovative medical students (r.0.64) to solve problems (r.0.52), with medical values (r.65).
Recognize the need to develop teaching competences is an achievement. According to the results of this research, teacher promotes students to be creative, innovative and resolve health problems articulating knowledge from different disciplines.
Medical professionalism is a teacher´s competence that contributes to ethical and humanistic performance of physicians. However for the development of this competences is necessary that teachers promote their human development (AMFEM, 2012) through analyzing his performance from a metacognitive process. First of all it is important to develop teaching competences proposed by AMFEM (2012) in a process of continuous training.

 Send Email
Send Email